Digital transformation is changing the manufacturing industry. It enables companies to increase productivity, make data-driven decisions, and increase efficiency. In this post, we will go over the benefits of digital transformation in manufacturing, some challenges manufacturers may face, and best practices. This post will provide a foundation for your digital manufacturing transformation journey.

Are you working on digital transformation at your plant? Let our Digital Transformation Roadmap guide your way.
What is Digital Transformation, and Why Does it Matter for Manufacturing?
Digital Transformation is the integration of digital technology into all sectors of manufacturing. It radically changes how companies function and gives value to their consumers. Digital transformation in the manufacturing sector refers to the use of technology to digitize and automate operations and enable data-driven decision-making. Ultimately, the goal is to improve efficiency, productivity, and profitability.
In today’s fast-paced digital economy, digital transformation helps manufacturers stay competitive and fulfill changing client expectations. Manufacturers may optimize operations and the supply chain, decrease costs, increase quality, and enhance customer experiences by embracing digital technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), software, and cloud computing.
Aside from increasing operational efficiency, digital transformation can lead to better agility and innovation. Manufacturers can quickly adjust to changing process conditions by employing real-time data insights and analytics.
The Impact of Digital Transformation on the Manufacturing Industry
Digital transformation has significantly impacted the manufacturing industry, revolutionizing the way companies operate and bringing unprecedented levels of efficiency and productivity. By embracing new technologies and software, manufacturers can streamline processes and make real-time data-driven decisions.
Benefits
Manufacturing companies can benefit in several ways by embracing digital transformation, including:
Increased OEE:
By automating processes and leveraging data-driven insights, manufacturers can streamline operations, reduce waste, reduce costs, and improve productivity, increasing OEE.
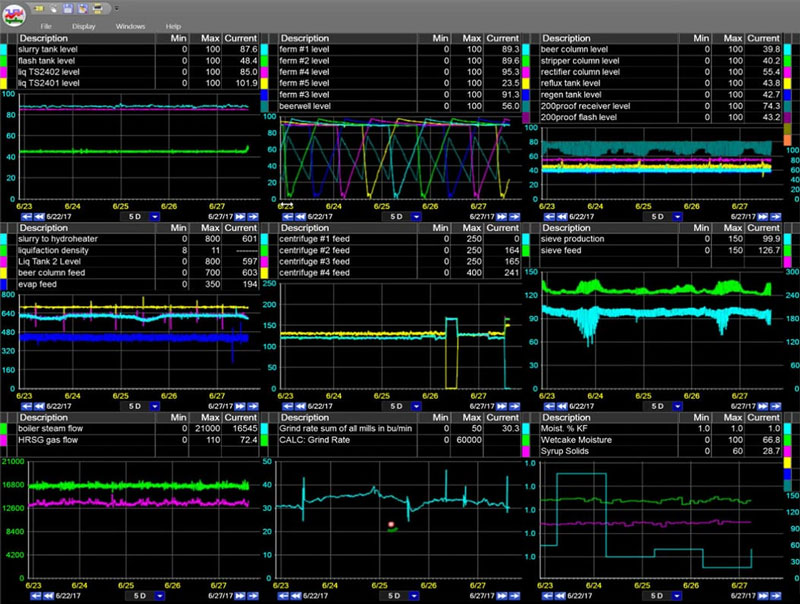
This is an example of a real-time production monitoring dashboard great for monitoring OEE and other KPIs.
Improved product quality:
LIMS, real-time data analytics, and machine learning software can help identify quality issues as they happen, enabling manufacturers to adjust and ensure products meet the customer demands and the highest standards.
Enhanced customer experiences:
By leveraging digital technologies to gain a deeper understanding of customer needs, preferences, and behaviors, manufacturers can deliver more personalized and relevant products and services.
Increased agility and innovation:
Access to real-time data can help manufacturers quickly adapt to changing process conditions and introduce new products and services, enabling them to stay on track and in production.
Improved collaboration and communication:
Data analysis and collaboration tools can help manufacturers better connect and communicate internally with partners, suppliers, and customers.
Challenges
Digital transformation doesn’t come without its challenges. Some manufacturers can experience:

See how Energy Transfer successfully underwent a complete digital transformation with dataPARC.
Legacy systems:
Many manufacturing companies still rely on legacy or internally created systems and processes. This can make it difficult to integrate with new technologies. Updating these systems can be costly and time-consuming.
Lack of digital skills:
Some manufacturing companies can lack the in-house digital expertise needed to effectively implement digital transformation initiatives. This can make it difficult to identify the right technologies to adopt and to manage the implementation process.
Resistance to change:
Resistance to change can be a major challenge when implementing new technologies in manufacturing. This can come from employees who are comfortable with traditional ways of working or from managers and business leaders who are hesitant to invest in new technologies without a clear return on investment.
Cybersecurity:
As manufacturing becomes more connected through digital technology, cybersecurity becomes increasingly critical. Manufacturers must ensure that they have adequate security measures in place to protect against cyber assaults and data breaches.
Cost:
Implementing digital transformation initiatives can be expensive, particularly for smaller manufacturers who may not have the same level of resources as larger organizations. Manufacturers need to balance the cost of implementation against the potential benefits carefully. Researching scalable technology is important, especially at the beginning of one’s digital transformation journey.
Overall, manufacturers face a wide range of difficult challenges while undertaking digital transformation. Overcoming these problems necessitates a methodical and deliberate approach, a willingness to accept change, and a dedication to acquiring the digital skills and experience required to flourish in a fast-growing digital economy.
Manufacturing Digital Transformation Drivers
The successful implementation of digital transformation in manufacturing relies on both people and technology. While technology provides most manufacturers with the necessary tools to automate processes and streamline operations, people drive innovation and create the culture needed to support and sustain change. By combining the right technology with a culture of innovation and continuous improvement, manufacturers can create a powerful engine for growth and transformation.

People
People are crucial in driving manufacturing digital transformation, both in terms of the skills and expertise they bring to the table and their actions to accomplish digital transformation efforts. Here are some examples of how people can help promote industrial digital transformation:
Leadership:
Driving digital transformation in manufacturing requires effective leadership. Leaders must have a thorough understanding of digital technologies and how they might be implemented in the context of manufacturing. They must also be able to communicate a clear digital strategy and goal and provide the resources and support required to make it a reality.
Skills and knowledge:
Manufacturing organizations must acquire workers with the appropriate digital skills and competence to achieve their digital transformation goals. This comprises data scientists, engineers, IoT specialists, and other digital professionals who can assist in identifying and implementing digital transformation opportunities.
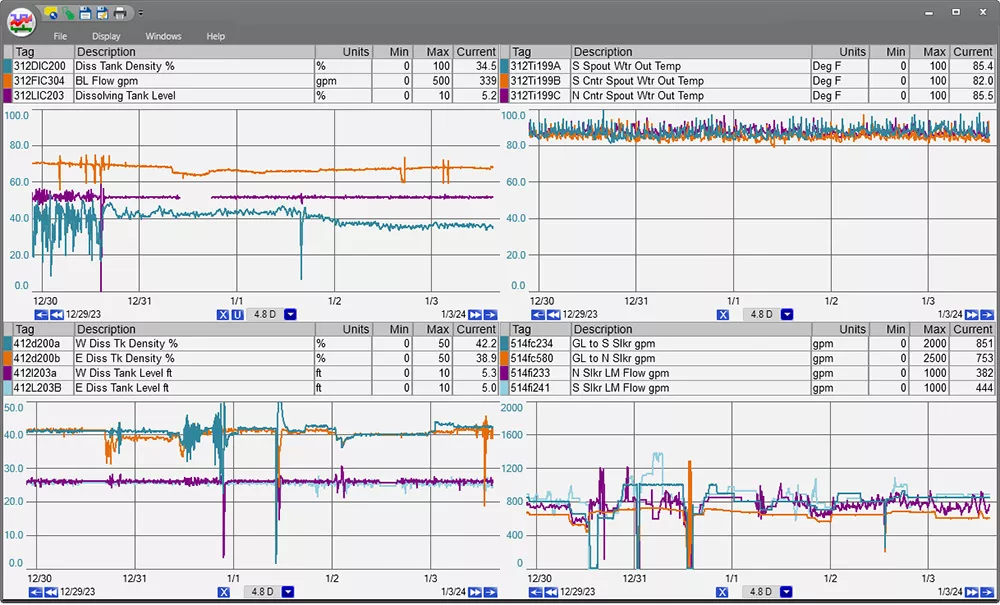
PARCview’s intuitive trend display has users interacting and creating new trends in minutes.
Communication:
Digital transformation is a team effort, and effective collaboration and communication is essential. Employees need to be able to work together across departments and functions to identify opportunities for digital transformation, develop and implement digital strategies, and share knowledge and best practices.
Change management:
Change management is an important part of digital transformation in manufacturing. Employees need to be prepared for the changes that come with new technologies, and leaders need to communicate the benefits and value of these changes to build buy-in and support.
Training and development:
To successfully implement digital transformation projects, manufacturers must invest in staff training and development.
Technology
Technology is another key driver of manufacturing digital transformation. Software and technology enable manufacturing companies to digitize their processes and collect and analyze data. Having access to big data in manufacturing is becoming more important. They can leverage this data to optimize their operations and drive business growth. Here are some of the ways in which technology is driving manufacturing digital transformation:
Internet of Things (IoT):
IoT technologies include sensors and connected devices. This enables manufacturers to capture real-time data from their production processes and equipment. This data can be used to monitor performance, identify inefficiencies, and optimize operations by using data visualization software.
Data Visualization and Analysis software:
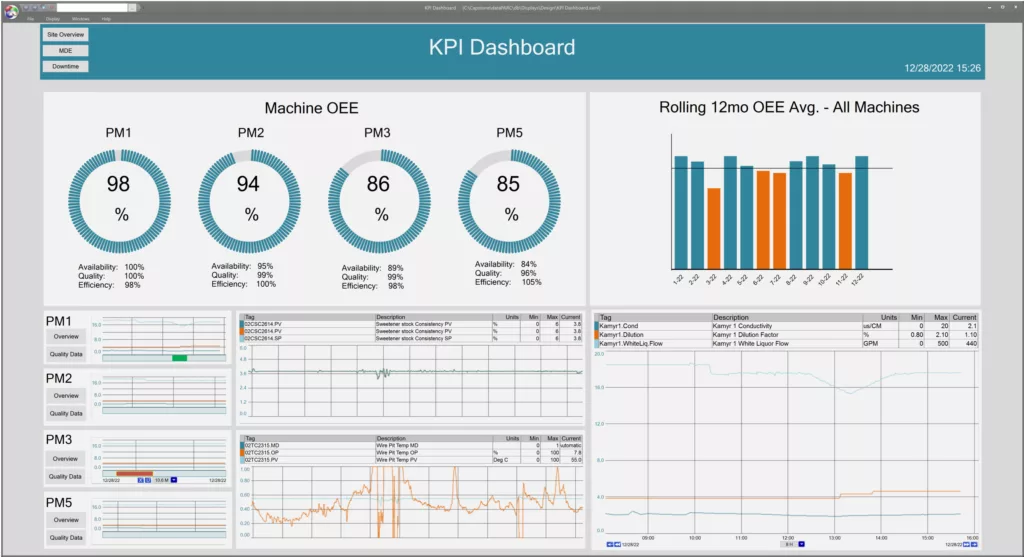
Data visualization software can help manufacturers make sense of large amounts of data. It can provide real-time insights into key performance indicators (KPIs) and help manufacturers identify areas for improvement. Visualization and analysis software, such as dataPARC, can allow manufacturers to make data-driven decisions and drive continuous improvement. Ultimately improving operational efficiency and reducing costs.
Cloud Computing:
Cloud computing allows manufacturers to store and process large amounts of data without needing to purchase expensive on-premises hardware. Additionally, it is a scalable, flexible platform, providing a gateway to digital transformation for even smaller companies on a budget. Cloud computing enables manufacturers to conduct data analysis and leverage other advanced technologies.
Enterprise Resource Planning Systems (ERP):
ERP systems are used to manage and automate inventory tracking, production schedules, purchasing and more. It gives companies a single source of truth, eliminating data silos and increasing collaboration across departments.
Quality Management Systems (QMS):
Quality Management Systems help track and ensure good quality products. Implementation of QMS software can improve operational efficiency, enhance product quality, and provide better traceability and compliance.
Implementing Digital Transformation in Manufacturing
Digital transformation has become a requirement for manufacturers looking to remain competitive in today’s fast-paced market. Implementing successful digital transformation often necessitates a cultural transformation, the use of new technologies, and the rethinking of corporate processes. Above, we outlined some challenges one can face when implementing new technologies, here we will walk through some steps to ensure a smooth transition.
1. Assess your Current Stage
Before implementing new ideas and technologies, you first have to assess your current stage in your digital transformation journey. This can be done by analyzing your current level of automation, the availability and quality of data, the level of integration across your systems, and the effectiveness of your analytics and decision-making capabilities. By understanding where you are on the digital transformation journey, you can identify gaps, prioritize investments, and create a roadmap for future growth and innovation. For details on the stages of digital transformation, check out: Digital Transformation Process Industries 5 Stages.
2. Identify your Goals
Knowing your current stage along the digital transformation path makes identifying your goals and creating a roadmap straight forward. To identify goals, research technology in known problem areas, reach out to your customers and look at your company’s strengths and weaknesses. Make sure the goals are clearly defined and S.M.A.R.T.

3. Create a Roadmap
Creating a roadmap for your digital transformation journey in manufacturing will keep the team focused and help stay on track. Since you have already identified your goals and assessed your current infrastructure, you can create a detailed plan for implementation. This plan should include a timeline for each stage of the process, milestones to measure progress, and specific KPIs to track success. It should also consider the resources and budget available, as well as any potential roadblocks or risks that may arise along the way.
4. Overcome Barriers to Implementation
Previously, we outlined some potential barriers that manufacturers may face when implementing new technologies, including resistance to change and use of legacy systems. To overcome these barriers, manufacturers can focus on building a strong digital culture, involving those who are going to use the technology and investing in the right technologies. Manufacturers can partner with technology vendors and consultants to identify and implement the right tools.
5. Measure and Monitor Success
Measuring and monitoring success in a digital transformation journey requires a strategic approach that includes establishing KPIs and monitoring progress over time. Cost savings, customer satisfaction, employee engagement and operational efficiency are common KPIs to monitor while working on a manufacturing digital transformation roadmap. For more on KPI monitoring, check out Building Effective Manufacturing Dashboards and Reports.
Manufacturing’s Future is Digital
There is no question that manufacturing facilities will have to employ new technologies to stay competitive. By embracing digital transformation and implementing it effectively, manufacturers will see increased productivity, efficiency, and agility. Setbacks may arise, but with a very clear vision and digital strategy, investment in the right technology, and a culture of innovation, manufacturers can navigate the challenges of manufacturing digital transformation and achieve their goals for growth and innovation.
FAQ: Digital Transformation in Manufacturing
1. What is digital transformation in manufacturing?
Digital transformation in manufacturing refers to the integration of digital technologies into all areas of production and operations. It includes modernizing systems, enhancing data access, and utilizing real-time analytics to improve efficiency, flexibility, and informed decision-making.
2. Why is digital transformation necessary for manufacturers?
It enables companies to stay competitive by improving operational performance, reducing downtime, increasing data visibility, and adapting quickly to market changes. It also lays the foundation for advanced capabilities, such as predictive maintenance and smart automation.
3. What are some examples of digital transformation in the manufacturing industry?
Examples include real-time dashboards for plant-wide visibility, IoT-enabled sensors tracking equipment health, centralized data platforms that connect lab and process data, and predictive models that alert operators before failures occur.
4. How does digital transformation impact plant operations?
It improves access to data across departments, supports faster root cause analysis, enhances collaboration between teams, and allows operators to monitor performance in real-time, leading to more proactive and informed decisions.
5. What are the common challenges in implementing digital transformation?
Challenges include legacy systems that don’t integrate easily, siloed data, limited internal resources, a lack of data context, and organizational resistance to change. That is where highly flexible software like dataPARC can help mitigate these challenges.
6. How can dataPARC support digital transformation initiatives?
dataPARC simplifies digital transformation by connecting to diverse data sources, contextualizing data across departments, and providing intuitive tools like real-time dashboards, manual data entry displays, and integration with advanced analytics tools.
7. How long does digital transformation take in manufacturing?
It depends on the scope, but many companies see measurable results within months of starting small. A full-scale transformation can take years, but building momentum through targeted projects ensures continuous progress and adoption.