This blog explores four strategic steps to improve manufacturing efficiency: engaging workers, harnessing data intelligence, enhancing scheduling efficiency, and optimizing processes with Six Sigma. Each section provides practical insights on implementation and benefits, illustrating how these strategies can lead to increased output, improved quality, cost reductions, and a safer, more sustainable manufacturing environment.
- Engage Your Workers
- Harness Data Intelligence
- Enhance Scheduling Efficiency
- Optimize with Six Sigma
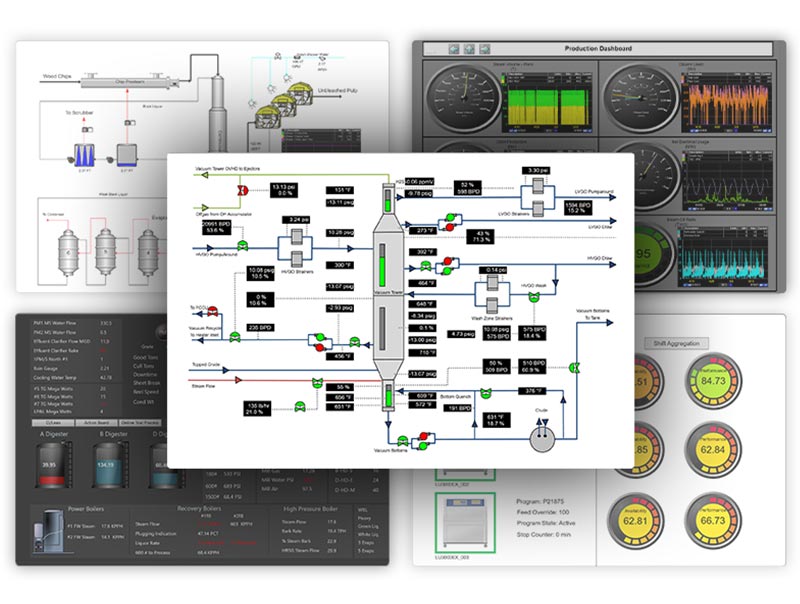
Monitor, report, & analyze production loss from unplanned downtime, poor quality, and performance issues.
Manufacturing Efficiency vs. Productivity
In manufacturing, efficiency and productivity are often used interchangeably, yet they encapsulate distinct aspects of the manufacturing process. Grasping these differences is crucial for any manufacturer aiming to optimize operations and reduce costs.
Defining Manufacturing Efficiency
Manufacturing efficiency focuses on how well resources are utilized to produce an output. It’s not merely about the quantity of output but about the optimal use of inputs to achieve that output. Efficiency is measured by comparing the actual output to the potential output within a given timeframe, with fewer resources wasted signifying higher efficiency. In essence, it’s about doing more with less, whether that’s in raw materials used, time, or energy.
Understanding Productivity in Manufacturing
Productivity, on the other hand, is a broader measure, typically focusing on the volume of output over a specific period relative to the input used. It’s about the rate at which products are created and doesn’t necessarily account for the resources expended. Higher productivity means more is being produced, but it doesn’t always imply that this is being done in the most resource-effective way.
Output: The Common Denominator
While efficiency and productivity have their nuances, both aim to enhance the output — the heart of any manufacturing operation. The output is the tangible result of your manufacturing process, whether it’s parts, products, or services. Improving efficiency might mean reducing waste or downtime while boosting productivity could involve increasing your material yield or output rate or improving worker performance.
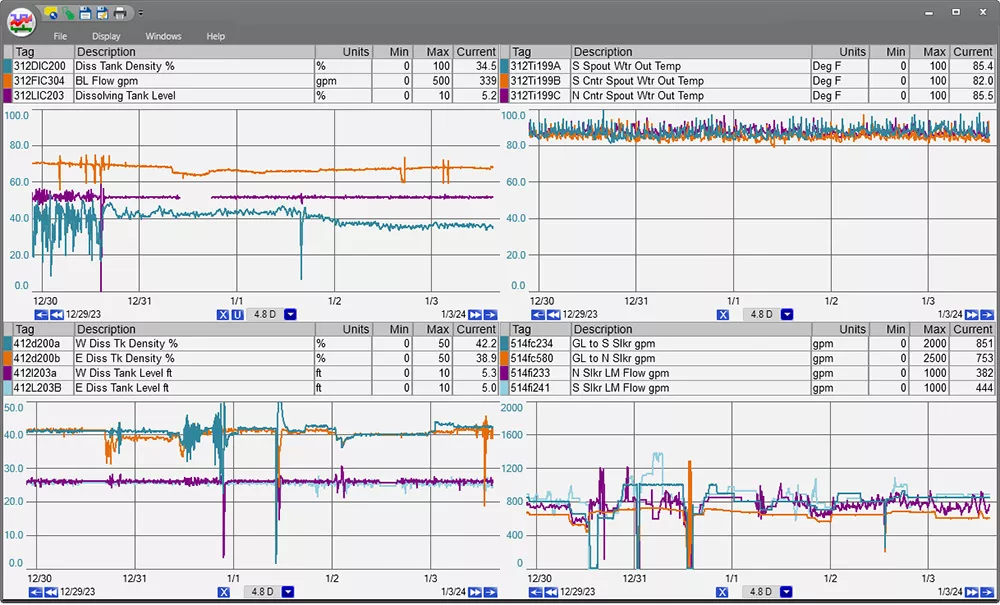
Visualize your manufacturing success with multi-trends: Track and optimize your efficiency and productivity in real time. See how changes in your process directly impact output, helping you make informed decisions to enhance production quality and performance.
By clearly defining and measuring both manufacturing efficiency and productivity, businesses can identify specific areas for improvement. For instance, dataPARC’s manufacturing process optimization software can be a pivotal tool in this journey, providing the insights needed to distinguish between efficiency and productivity outcomes and to implement strategies that enhance both.
Steps to Improve Manufacturing Efficiency
Step 1: Engage Your Workers
Engaging your workers involves creating a culture of inclusivity and involvement. Encourage feedback, foster open communication, and provide opportunities for employees to contribute to decision-making processes. Implementing recognition programs and providing clear paths for career advancement can also enhance engagement.
The key to the success of any efficiency-improvement project lies in gaining your operators’ buy-in. When employees are engaged and feel valued, they’re more likely to collaborate effectively, embrace changes, and participate actively in training programs.
This foundational step ensures that subsequent efficiency initiatives are met with enthusiasm rather than resistance, leveraging collective effort toward common goals. By emphasizing that efficiency improvements are aimed at optimizing their time, allowing them to focus on more preferred tasks, you align their personal interests with organizational objectives.
Step 2. Harness Data Intelligence
To harness data intelligence, implement systems that gather, analyze, and interpret data relevant to your manufacturing processes. Utilize manufacturing analytics software that provides real-time insights and facilitates data-driven decision-making.
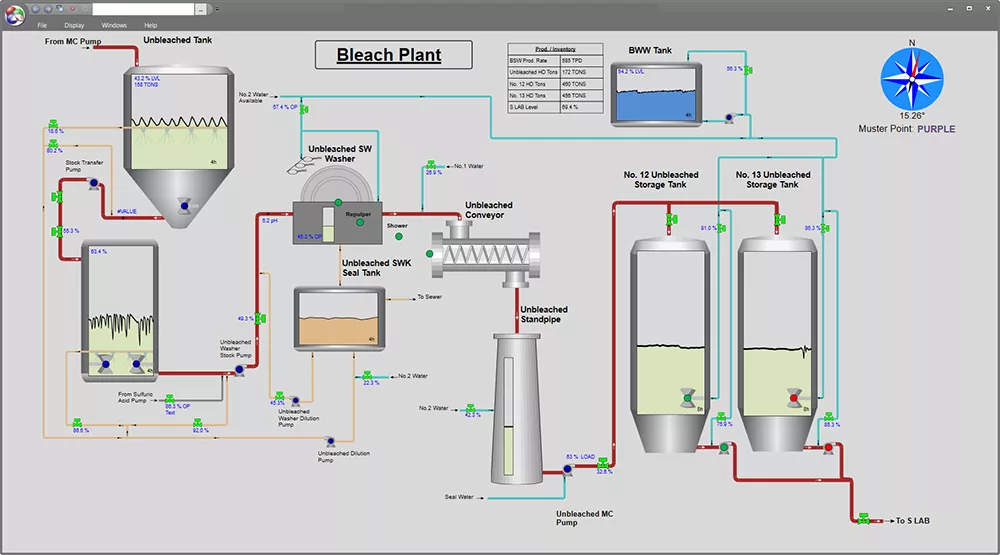
Experience real-time clarity with dataPARC’s dynamic graphics for production monitoring. Data can be trended with a click, empowering you with instant insights directly at your fingertips.
Without accurate data, identifying areas for improvement becomes a shot in the dark. Data intelligence tools can significantly amplify your manufacturing efficiency by pinpointing inefficiencies, predicting potential issues, and guiding strategic decisions. This step ensures that your efforts to boost efficiency are informed, targeted, and effective.
Step 3. Enhance Scheduling Efficiency
Review and optimize your production scheduling and supply chain management. Utilize advanced scheduling software to align production with demand, reduce bottlenecks, and improve material flow. Assess your supply chain for potential enhancements in delivery times, inventory management, and supplier relationships.
Before delving into process changes, it’s crucial to streamline upstream elements like scheduling and supply chain management. Inefficiencies in these areas can undermine process improvements, causing delays and increased costs. By optimizing scheduling and supply chain operations first, you set a solid foundation for more focused process improvements, ensuring that changes in your production lines are supported by efficient and responsive upstream operations.
Step 4. Optimize with Six Sigma
Implement Six Sigma methodologies to systematically reduce or eliminate waste, improve quality, and enhance efficiency. Start with defining goals, measuring current performance, analyzing data, improving processes, and controlling outcomes to maintain advancements.
Embarking on Six Sigma projects without addressing the first three steps might lead to inefficiencies. By starting with worker engagement, data intelligence, and scheduling enhancements, you create an environment ripe for Six Sigma’s data-driven, meticulous approach to continuous improvement. Once you have buy-in, the necessary data, and an optimized upstream environment, Six Sigma can effectively reduce waste and refine processes, ensuring sustainable improvements in manufacturing efficiency.
By following these four strategic steps, manufacturers can create a holistic approach to efficiency improvement, driving significant gains in productivity, quality, and overall performance.
How to Measure Your Progress: Manufacturing Efficiency KPIs
Monitoring progress in improving manufacturing efficiency is crucial to understand the impact of implemented changes and guide further improvements. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) provide the metrics needed to evaluate effectiveness across various aspects of manufacturing. For more about KPI’s check out Manufacutring KPI Examples: 10 Formulas for Measuring Success.
Equipment
Understanding metrics not only sheds light on current equipment effectiveness but also guides strategic decisions for future improvements. Here’s how you can leverage specific KPIs to assess and enhance your equipment’s performance:
Changeover Time:
Minimizing the time required to switch equipment from producing one product to another enhances operational flexibility and reduces idle time.
Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE):
This comprehensive metric combines availability, performance, and quality to provide a holistic view of equipment effectiveness. A higher OEE percentage indicates more efficient equipment usage, directly correlating with increased manufacturing productivity.

Everything you need to successfully implement, analyze, & improve overall equipment effectiveness.
Costs
By closely monitoring these metrics, businesses can pinpoint opportunities to enhance profitability, improve efficiency and streamline operations. Here’s how different cost KPIs come into play in manufacturing:
Cost Per Unit:
This metric calculates the total expense involved in producing a single unit, encompassing all direct and indirect costs. It serves as a fundamental indicator of manufacturing efficiency, guiding cost-reduction strategies, and pricing decisions.
Total Manufacturing Cost Per Unit:
This KPI provides a comprehensive view of all costs associated with manufacturing each unit, offering a baseline for identifying cost reduction opportunities across various production aspects.
Yield
In manufacturing, yield is a critical measure of production efficiency and product quality. Here’s an exploration of key yield KPIs and their significance in the manufacturing process:
Customer Return Rate:
While primarily a customer satisfaction metric, a high return rate can indicate underlying issues with product quality or production processes, affecting the yield and necessitating a closer examination of the entire manufacturing lifecycle.
First Pass Yield (FPY):
First pass yield, or the percentage of products that meet quality standards without requiring rework, is a direct indicator of process efficiency and quality control effectiveness. A higher FPY suggests that the manufacturing process is well-optimized, producing more units that are right the first time, reducing waste and improving overall production line efficiency further.
Overall Yield:
This broad metric reflects the total effective output as a percentage of the total units produced, encompassing all stages of the production process. It provides a comprehensive view of how well resources are converted into final products, highlighting the overall effectiveness of the manufacturing process.
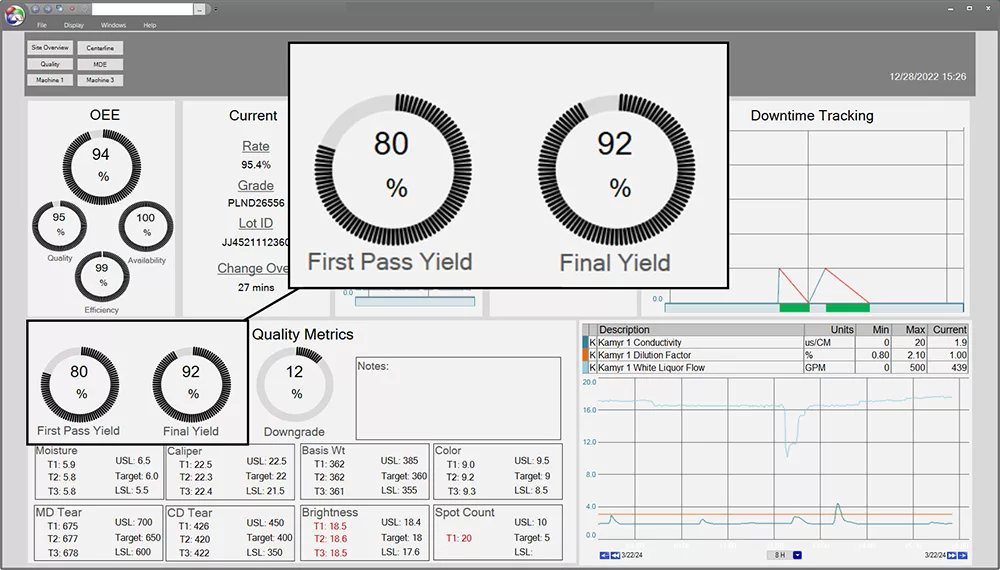
dataPARC graphic shows that users can visualize and monitor first pass yield and final yield alongside other key quality metrics. Identify deviations in real-time, analyze trends, and correlate yields with other operational parameters to swiftly pinpoint and address factors impacting production quality.
Labor
The efficiency and productivity of the labor force are pivotal for the success of manufacturing companies’ operations. Analyzing specific labor-related KPIs provides valuable insights into workforce performance and areas for improvement.:
Labor Efficiency:
This KPI evaluates the amount of output produced by the workforce over a specific period, offering insights into how effectively labor resources are utilized. By monitoring labor efficiency, manufacturers can identify opportunities to enhance training, streamline workflows, or adjust staffing levels to boost productivity.
Overtime:
While necessary at times, excessive overtime can indicate inefficiencies in workforce planning or process management. Tracking overtime helps assess whether current labor resources are aligned with production needs and can reveal underlying issues that may require attention, such as bottlenecks or inadequate staffing.
Employee Turnover Rate:
High turnover rates can lead to increased recruitment and training costs and disrupt the production line continuity. Monitoring this rate helps in developing strategies to improve employee retention and satisfaction, contributing to a more stable and experienced workforce.
Choosing the appropriate KPIs is pivotal as they provide the insights necessary to assess the performance of various manufacturing processes and identify areas for improvement. By carefully aligning KPIs with your plant’s specific goals and challenges, you can ensure that the metrics you monitor are directly relevant to your efficiency objectives.
Benefits of Improved Manufacuing Efficiency
The advantages of an efficient manufacturing plant extend across various dimensions, not only boosting the plant’s output and cost-effectiveness but also fostering a more sustainable, safe, and positive work environment. Here’s an expanded view of the benefits of lean manufacturing has:
- Increased Output and Productivity: Efficiency enhancements lead to standard output and a significant rise in productivity. An optimized plant can produce more goods in less time with optimal resource utilization, meeting market demands swiftly and expanding the business’s growth potential.
- Environmental Sustainability: Efficient plants contribute to sustainability by optimizing resource use and minimizing waste, resulting in reduced environmental impact. Energy-efficient operations cut down on costs and contribute to a reduction in carbon emissions, aligning the plant’s operations with broader environmental goals.
- Enhanced Safety: Efficiency and organization in a plant promote a safer working environment. Clear SOPs and regular maintenance reduce the risk of accidents, creating a safer workplace and minimizing potential operational interruptions.
- Improved Quality: Streamlined and monitored processes in an efficient plant to maximize efficiency and ensure higher product quality. Consistency in production methods leads to fewer defects, enhancing customer satisfaction and brand reputation.
- Cost Reduction: Efficiency translates into cost savings by minimizing waste, optimizing resource use, and improving process flows, allowing the company to reinvest savings or improve profit margins.
- Employee Retention: An efficient plant fosters a positive work environment where employees feel valued and productive. High efficiency often correlates with higher employee satisfaction, which can reduce turnover rates and associated training and hiring costs.
By embracing efficiency, a manufacturing plant not only enhances its operational metrics but also supports its workforce, the environment, and its capacity for growth and adaptation, creating a robust foundation for sustained success.









