Learn how to manage energy at your site, an increasingly vital strategy for industries aiming to optimize their energy use, cut costs, and minimize their environmental footprint. This post explores how to approach continuous monitoring, analysis, and improvements to transform energy consumption, boosting operational efficiency and sustainability.
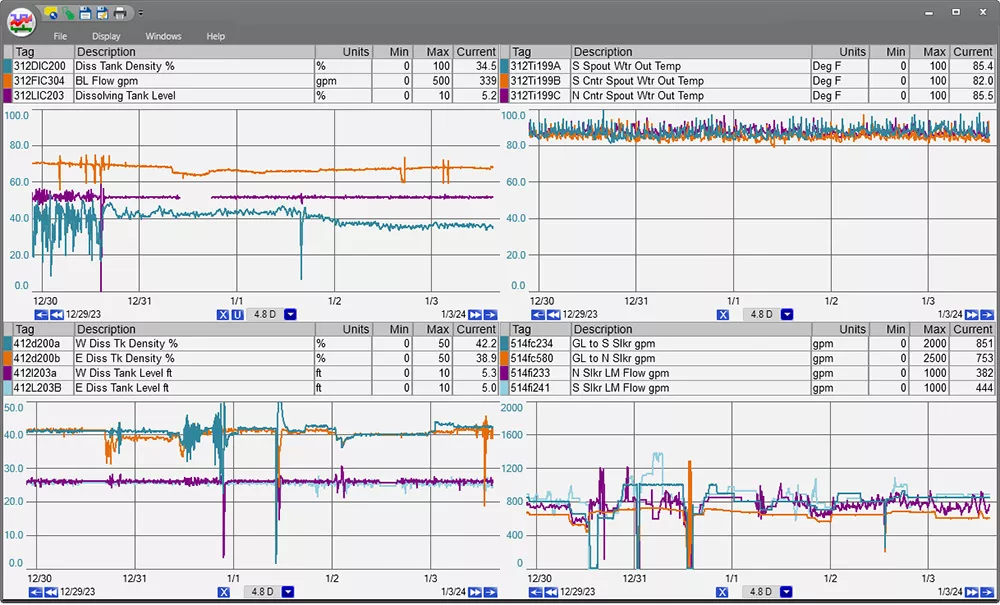
Check out our advanced analytics & monitoring tools to see how you can apply them to energy management at your site.
What is Industrial Energy Management?
Industrial Energy Management is a systematic approach to optimizing energy usage within industrial operations. It aims to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and minimize environmental impact. With today’s heightened environmental awareness and escalating energy costs, managing energy consumption has become a critical aspect of operational strategy for industries worldwide.
At its core, Industrial Energy Management involves continuously monitoring, analyzing, and improving energy use at a facility. This includes everything from machinery and equipment operation to heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, lighting, and beyond. The goal of industrial companies here is not merely to cut down on energy use haphazardly. It’s to make informed decisions aligning energy efficiency with production goals, ensuring energy consumption is optimized without compromising output quality or volume.
Key Components of Industrial Energy Management
Understanding the key components of industrial energy management is crucial, as they are the backbone of sustainable and efficient energy practices within the industrial sector.
- Energy Audits: A thorough assessment of energy flows and consumption within an industrial facility to identify opportunities for efficiency improvements.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Leveraging advanced software solutions, such as dataPARC, to track and optimize energy usage in real-time, allowing for immediate insights and adjustments.
- Performance Benchmarking: Comparing energy performance against industry standards or past data to identify areas for improvement.
- Energy Efficiency KPIs: Implementing targeted initiatives to reduce energy consumption, such as upgrading to more efficient equipment, optimizing operational practices, and enhancing process controls.
- Team Involvement: Fostering a culture of energy awareness and efficiency among staff at all levels, ensuring that energy management becomes an integral part of the organizational ethos.
By integrating sophisticated data analytics and visualization tools like dataPARC, industries can navigate traditional barriers to using energy management solutions. These technologies enable a granular view of energy consumption patterns. They allow users to identify inefficiencies and implement corrective measures. The result is a more sustainable, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly industrial operation.
Experience real-time energy monitoring with PARCview’s dashboard, where users can view energy usage instantly, incorporate trends, or click on values to analyze data over time.
In essence, Industrial Energy Management is not just about reducing energy bills or using energy resources in compliance with regulations; it’s about embedding energy efficiency into the fabric of industrial operations. It represents a strategic pivot towards a more sustainable industrial future, where energy is conserved as a valuable resource and operational efficiency is continually enhanced.
Benefits of Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency in industrial environments is not just about conservation; it’s a strategic approach that yields significant business benefits, both in terms of sustainability and cost savings. By optimizing energy use, industries can enhance operational efficiency, reduce environmental impact, and realize substantial savings.
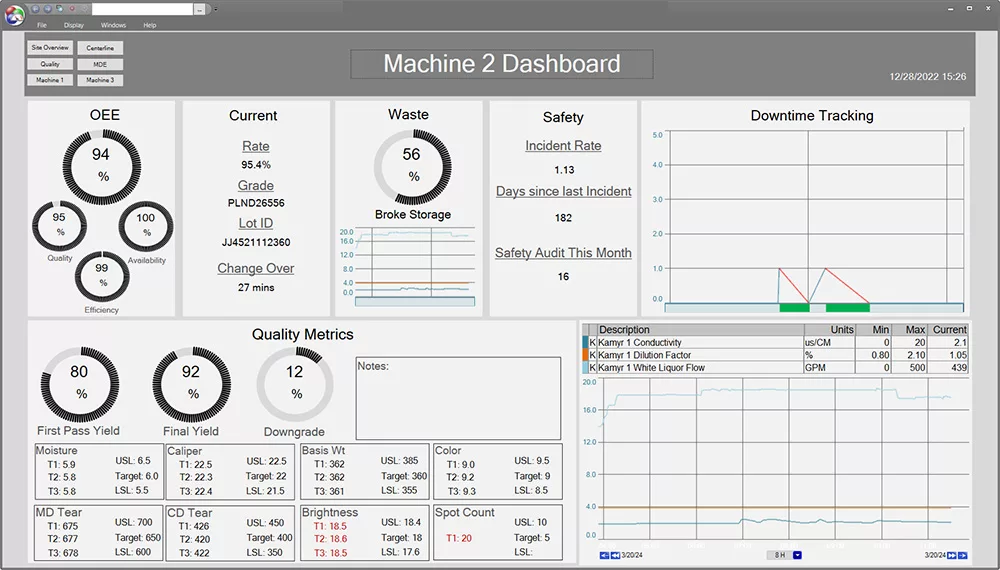
Build Real-Time Dashboards & Displays for Effective Process Monitoring with dataPARC
Sustainability: Enhancing Ecological Footprint
Adopting energy-efficient practices in industrial operations plays a pivotal role in reducing the ecological footprint of businesses. By minimizing energy consumption, industries can significantly lower their greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to a more sustainable and healthier planet.
This commitment to sustainability is an ethical choice and enhances a company’s image, bolstering its social reputation. In today’s environmentally conscious market, a strong commitment to sustainability can be a powerful marketing tool, attracting customers, investors, and talent who prioritize environmental responsibility.
Saving Money: Operational and Financial Benefits
The financial advantages of energy efficiency are twofold: direct savings on energy costs and indirect savings through operational improvements. Industries can significantly improve energy efficiency and reduce utility bills by using less energy, directly impacting their bottom line. Moreover, energy-efficient practices often lead to enhanced operational efficiency. Optimized energy use can result in smoother, more efficient production processes, reducing waste and increasing productivity.
Furthermore, compliance with industrial energy efficiency regulations is crucial in avoiding potential fines and penalties. As governments worldwide tighten environmental regulations, adherence to energy efficiency standards becomes crucial. By proactively embracing energy-efficient practices, industries can ensure compliance, avoiding costly fines and reinforcing their commitment to sustainable practices.
Energy Management Metrics: Key Performance Indicators for Efficiency
Tracking the right metrics is essential to pursuing effective industrial and energy management programs. These metrics not only provide insights into current energy usage but also guide strategies for improvement. Here’s a closer look at the key energy management metrics and how to calculate them:

Achieving Environmental Excellence: Your guide to environmental KPIs, strategic practices, and more!
Energy Consumption by Date
This metric tracks the amount of energy consumed over specific periods, offering insights into usage patterns and identifying peak consumption times.
Calculation: Total energy consumed within a specified date range. This can be daily, weekly, monthly, or annually, measured in units relevant to the energy source (kWh for electricity, therms for gas, etc.).
Energy Spend vs. Budget
Comparing actual energy expenditure against budgeted amounts helps in financial planning and identifying areas where energy costs exceed expectations.
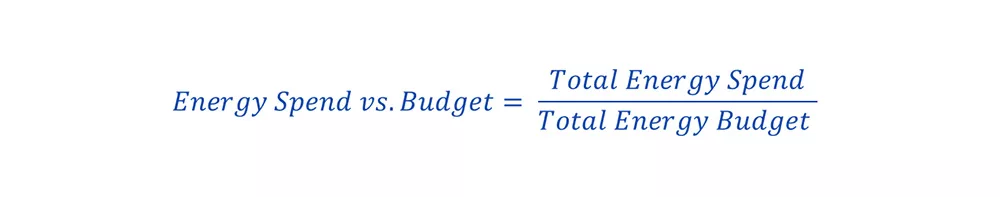
Calculation: Total energy spent for a given period compared to the budgeted or forecasted amount for the same period. This involves summing up all energy costs and comparing them to the budget allocations.
Carbon Intensity
Carbon intensity measures the amount of carbon dioxide emissions per unit of energy consumed, indicating the environmental impact of energy use.

Calculation: Total CO2 emissions divided by total energy consumed. Emissions factors specific to each energy source are used to convert energy consumption into CO2 equivalents.
Production-Normalized Energy Intensity
This metric assesses energy efficiency in relation to production output, providing a fair comparison across different operational scales.
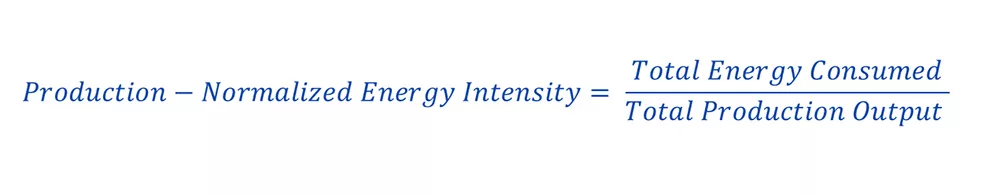
Calculation: Total energy consumed divided by the total production output. This normalizes energy use against production volume, allowing for comparisons over time or between different facilities.
Energy Savings for the Current Year
Tracking the energy saved due to efficiency measures compared to a baseline year highlights the effectiveness of energy management strategies.
Calculation: Difference in energy consumption between the current year and a baseline year, adjusted for any relevant variables that might affect energy use (such as changes in production volume or facility size).
Annual Improvement in Energy Intensity
This metric measures the year-over-year improvement in energy efficiency, reflecting the progress in reducing energy consumption relative to production.
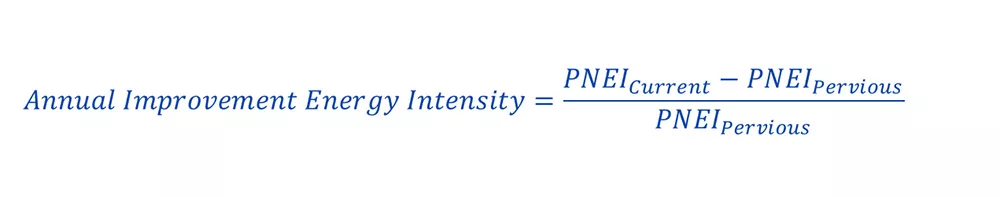
Calculation: The percentage change in production-normalized energy intensity (PNEI) from one year to the next. A negative value indicates an improvement in energy efficiency.
Leveraging software to automate these calculations can greatly enhance the efficiency of tracking and analyzing key metrics. A platform capable of gathering and presenting data in real-time while performing these calculations is invaluable.
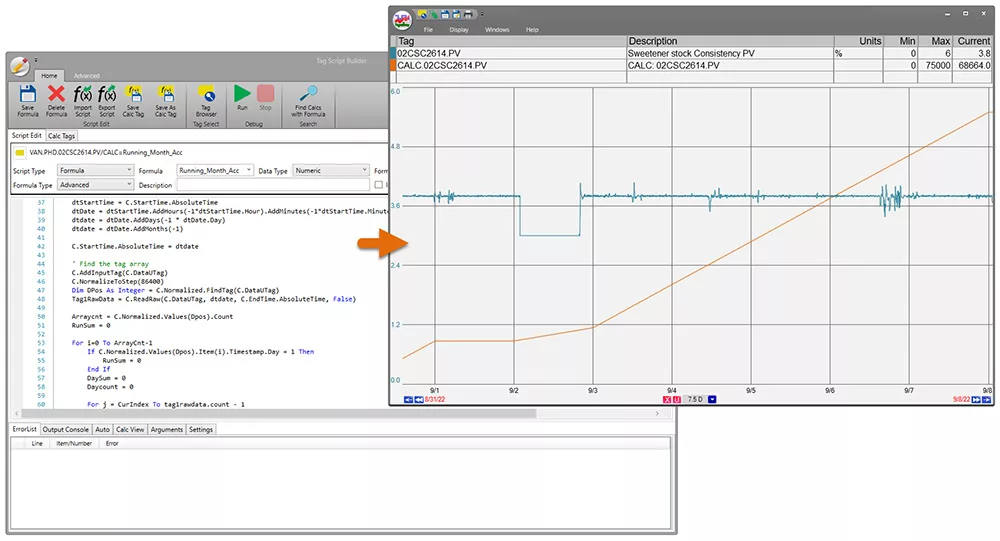
Effortlessly transition from calculations to trends in PARCview with a simple click and drag. dataPARC’s calc script editor and trend window make data analysis seamless and user-friendly.
dataPARC serves as an exemplary tool in this context. With its advanced data visualization and analytics capabilities, dataPARC empowers industries to precisely monitor their energy performance, discern patterns, and execute strategies rooted in data to boost energy efficiency and promote sustainability.
Improving Energy Management – A Continuous Effort
Optimizing energy management systems in industrial settings involves a multifaceted approach, focusing on data-driven decisions, equipment upgrades, insulation improvements, and process optimization. Each of these aspects plays a crucial role in enhancing overall energy efficiency.
Data Collection and Integration
At the core of effective energy management is collecting and analyzing accurate data. dataPARC software offers comprehensive manufacturing analytics capabilities, enabling businesses to gather real-time energy data from various parameters. This data provides insights into current energy usage and identifies potential areas for efficiency improvements.
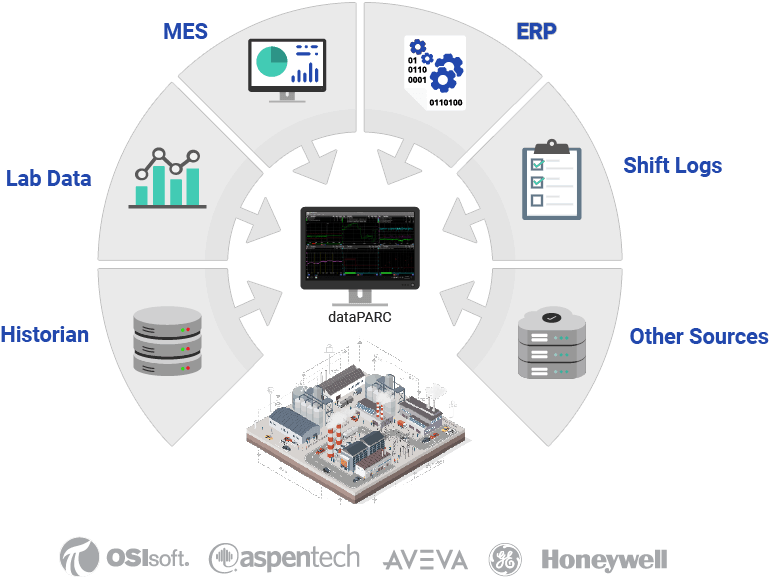
dataPARC optimizes vast datasets for high-speed, real-time analytics, enabling you to connect and aggregate data from multiple systems or sites, ensuring enterprise-wide visibility and streamlined decision-making.
By leveraging manufacturing data integration into these analytics, companies gain a comprehensive view, allowing them to make informed decisions, tailor their energy-saving strategies, and effectively monitor the impact of implemented changes, thereby fostering a culture of continuous improvement and operational excellence.
Upgrade Equipment and Technologies
Investing in modern equipment, services, and technologies can lead to significant energy savings:
- Lighting: Switching to energy-efficient lighting systems, such as LED, can drastically reduce energy consumption while maintaining or improving lighting quality.
- Motors, Pumps, and Compressors: Upgrading to high-efficiency models can see manufacturers enhance performance and reduce energy use. These components are often used extensively in industrial operations, and even small efficiency improvements can result in substantial savings.
- Software Optimization: Ensuring plant management software is up-to-date is vital. Modern software solutions can optimize operational settings to minimize energy waste and incorporate current best practices for energy management.
Improve Insulation
Enhancing insulation is a cost-effective way to conserve energy:
- HVAC Systems: Proper insulation of HVAC systems reduces energy loss, maintaining desired temperatures with lower energy input.
- Equipment Insulation: Insulating industrial equipment minimizes heat loss or gain, improving efficiency and reducing energy requirements.
- Programmable Thermostats: Implementing programmable thermostats allows for better control of heating and cooling systems, ensuring energy is used only when needed and optimizes energy resources.
Optimize Processes
Process optimization is key to reducing energy consumption without compromising output:
dataPARC provides valuable insights into operational processes, identifying inefficiencies and areas where energy use can be minimized. Alarms can be set, and users are notified when a parameter is beyond its limit.
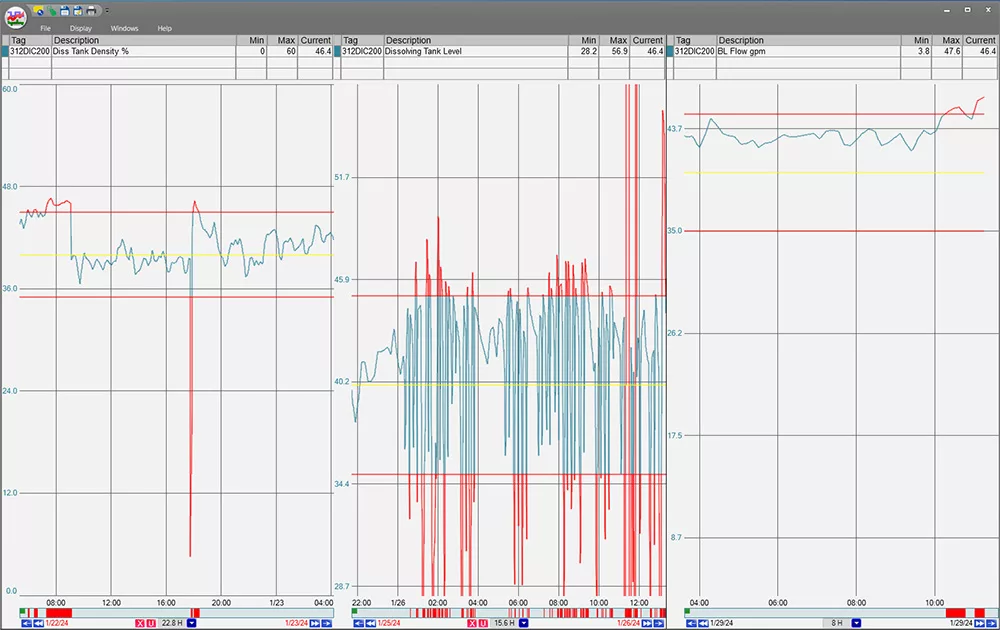
Discover the power of multi-trend analysis in PARCview, where integrated limits clearly indicate when your process variables stray from the optimal range, guiding you toward precise process optimization.
By continuously monitoring process parameters, dataPARC helps maintain optimal conditions, ensuring energy is used as efficiently as possible. This leads to energy savings and enhances overall operational efficiency and productivity.
Through these strategic approaches, businesses can significantly improve their energy management practices. By combining data-driven insights with technological upgrades and process optimizations, industries can achieve substantial energy savings, contribute to environmental sustainability, and realize financial benefits from reduced operational costs.
Takeaways on Industrial Energy Management
As industries continue to evolve and environmental standards become increasingly stringent, the importance of a proactive approach to energy management cannot be overstated. Integrating advanced software like dataPARC and other tangible upgrades in equipment and operational practices can help your site be more energy efficient. These strategies underscore the commitment to the environment and unlock significant economic advantages, balancing operational excellence with ecological responsibility.
FAQ: Industrial Energy Management
1. What is industrial energy management?
Industrial energy management is the process of monitoring, controlling, and optimizing energy use within a manufacturing or processing facility. It focuses on reducing waste, improving efficiency, and lowering operational costs while maintaining production quality.
2. Why is energy management critical in manufacturing?
Energy costs often account for a significant portion of operational expenses. Effective energy management helps reduce utility bills, decrease environmental impact, and improve overall plant performance and profitability.
3. What are the biggest energy users in industrial facilities?
Common high-energy consumers include boilers, compressors, motors, HVAC systems, and production equipment. Identifying these areas is key to targeting improvement efforts.
4. How can I start tracking energy usage in my facility?
Begin by identifying major energy consumers and installing meters or sensors to monitor real-time usage. Integrating this data into a centralized system, like dataPARC, allows you to visualize consumption trends and find opportunities for improvement.
5. What challenges do manufacturers face when managing energy?
Challenges include a lack of real-time data, disconnected systems, limited resources to analyze energy trends, and resistance to changing long-standing processes. A user-friendly system that brings data together in one place can help overcome these barriers.
6. What metrics should I track for energy efficiency?
Key metrics include total energy consumption, energy cost per unit produced, specific energy use (kWh/ton or BTU/lb), boiler efficiency, and usage per equipment or area. Tracking these over time helps identify areas for improvement.
ESG Environmental Excellence Guide
A comprehensive guide focusing on key environmental KPIs, strategic practices, and how software can support impactful environmental strategies for sustainable operational success.









