All forms of commerce require energy and industrial energy monitoring is essential. Industrial processing facilities tend to be the largest consumers. Even service industries such as insurance and banking services require large buildings which must be heated, cooled and lit.
The newest large energy consuming enterprises are data centers. Data centners are large clusters of computers which store and serve up the data which flows through the internet. Regardless of the end use or the industry, companies strive to minimize production costs by minimizing energy consumption.
In addition to economic incentives, it is increasingly accepted that every BTU that is generated by burning fossil fuels (the source of the majority of our energy) leads to an increase in atmospheric carbon dioxide. This, in turn, appears to be causing some undesirable changes in the global climate. There are now more reasons than ever to focus on energy monitoring in manufacturing.

Achieving Environmental Excellence: Your guide to energy and environmental KPIs, strategic practices, and more!
Benefits of Industrial Energy Monitoring Systems
Implementing an industrial energy monitoring system offers numerous advantages for manufacturing operations. These systems help lower production risks and improve energy efficiency by providing real-time monitoring and control, ensuring smooth and uninterrupted operations. Such systems enhance operational efficiency but also significantly boost energy efficiency.
Energy Management Systems help speed up time to market by optimizing energy usage and reducing delays associated with energy inefficiencies. Reducing energy costs is another significant benefit. Since energy monitoring systems identify areas where energy can be saved, leading to lower utility bills and operational expenses.
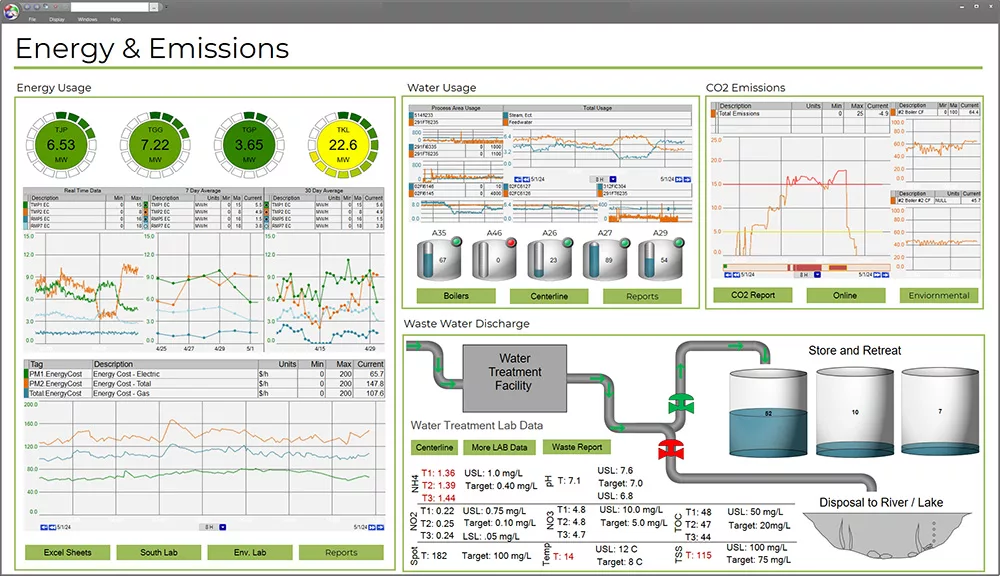
Real-time monitoring software allows for integrated energy dashboards. Providing all your data in one place. This makes it easy to monitor and manage energy consumption for improved efficiency and sustainability.
Additionally, these systems and devices support sustainability initiatives by reducing energy consumption and associated carbon emissions, contributing to a greener and more sustainable manufacturing process. With energy monitoring, environmental monitoring follows closely behind. You can use a single system to manage both, ensuring comprehensive oversight of your sustainability efforts.
Energy Monitoring In Manufacturing
Effectively reducing overall energy consumption requires planning and corporate-wide commitment. For example, consider a product that is dried in a natural gas-fired dryer, subsequently cured, brought to a final dryness in an electric dryer, and then coated.
If an individual manager reacted to a “mandate to save energy,” he or she might reduce the amount of gas used in the first dryer. This action, however, might interfere with the curing process and would increase the load in the electric dryer. This is incrementally more expensive to use than the gas dryer. One isolated action would result in a higher total energy use. Plus, higher production cost and perhaps lead to some product quality problems.
This type of misstep can be avoided through the development of an energy management and montioring program. The goal of such a program is to sustainably manage and reduce energy use throughout a business, and it consists of two important components.
Collection & Analysis Of Energy Data
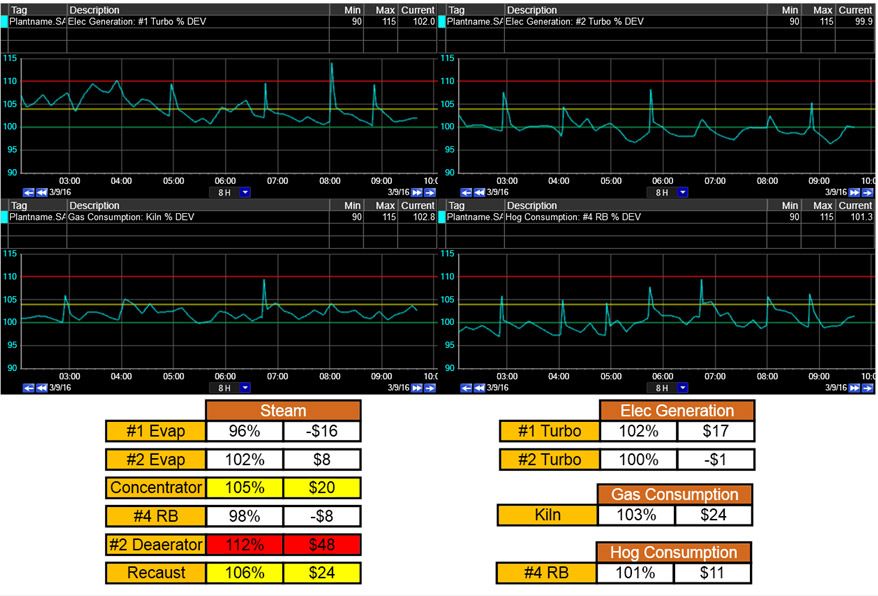
Data analysis software, like dataPARC’s PARCview can be used to collect, monitor and analyze energy data.
he backbone of an industrial energy efficiency and management program is the collection and analysis of energy data. Being able to quantify the current levels of energy consumption and measure future improvements is essential. Industrial energy management software should be able to:
- Collect data from a variety of sources (i.e. discrete meters, DCSs, PLCs, databases, other data collection systems)
- Compile data from multiple plant sites, if needed
- Store (or historize) the collected data
- Show current and historical data in meaningful and clear displays
- Provide tools for data analysis
Administration
In addition to the data handling system, a significant administrative and social element is required for comprehensive energy management in manufacturing, as reducing energy consumption requires change. Plants have historically relied on passive methods, installing a more efficient motor or insulating a heated tank, to reduce energy, where savings will happen automatically once installed. However, convincing operators to report compressed air leaks or to control processes more efficiently, activities which require their ongoing participation, requires good communication of goals and some retraining.
For these reasons, upper management must be involved and committed to the goal of improving energy efficiency and reduction. Furthermore, the goals and actions of the program must be clearly communicated to everyone in the company who will be implementing them, or are affected by the changes. Training and understanding are crucial to the overall success of this type of program.
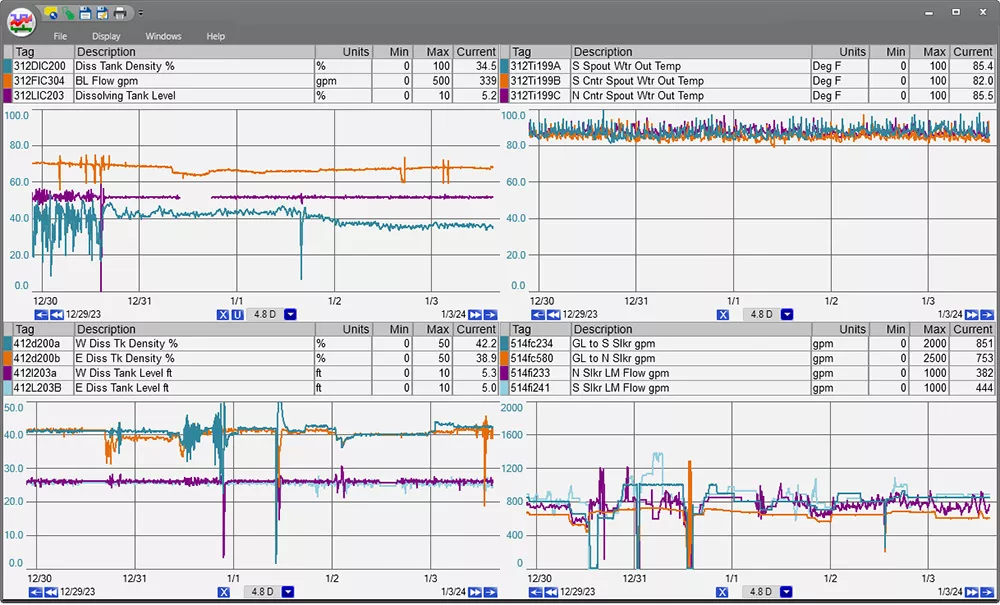
Monitor and analyze energy trends effortlessly with our user-friendly trend visualization tools, providing clear insights for better administration and decision-making.
Once goals have been set and changes implemented, data can be reviewed to observe the effectiveness of the changes. Whether a group of initiatives are successful or not, new ideas and solutions for energy use reduction will probably come to light, and other changes can be implemented. Changes within the process and changes in the cost and availability of external energy supplies mean that energy use optimization must be an ongoing process.
Implementing An Industrial Energy Monitoring Solution Using ISO 50001
One approach to implementing a manufacturing energy management and monitoring program is to use the International Organization for Standards guidelines for energy saving, or ISO 50001-2011. This standard lays out requirements for policies, procedures, tools, and techniques to implement an effective energy management program. The objective of the standard is to integrate energy management into all parts of an organizational culture, and to avoid having an “energy saving program” be a short term initiative handled by only certain departments, such as engineering or accounting. In addition to company-wide involvement, part of the ISO standard specifies that there also needs to be continual improvement in both the program and the actual energy savings.
The ISO 50001 standard takes a structured, integrated and systematic approach toward achieving energy performance improvements using a “Plan-Do-Check-Act” improvement framework:rgy performance improvements using a “Plan-Do-Check-Act” improvement framework:
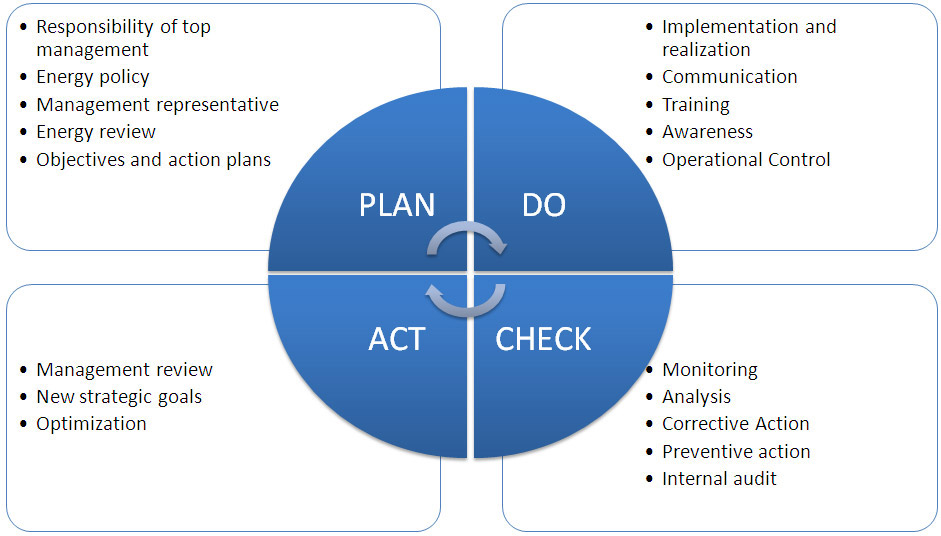
ISO standard framework. Image credit Wikipedia.
Plan
The first step toward implementing an energy program is to create a plan. This step can be described in two phases. In the first phase, top management must commit to the concept of energy reduction and develop a framework for implementation. The framework includes defining the scope, creating policies and goals, and developing a team of people to lead or undertake the required work. When all these pieces are in place, the importance of what is being done needs to be communicated to everyone within the organization.
The second phase of the planning step involves collecting and reviewing data. The goal of this work is to understand the current state of operation and identify areas of significant energy consumption. Based on this knowledge, strategies for energy reduction are proposed.
Do
In this step, actual energy management and reduction actions are implemented. New, energy efficient equipment may be purchased at this point. Energy saving procedures are put into place. Responsible individuals are assigned and workers are retrained if necessary. Alternate external energy sources may be found and implemented in response to cost or environmental concerns.
Check
An energy management program requires a process for determining if it is being cost effective. Internal audits should look at the administrative aspects of the program itself to determine if it has any deficiencies, and to determine if it is being correctly implemented. Energy data also needs to be reviewed to determine the effectiveness of the program regarding actual energy consumption. Deficiencies in the administration or performance of the program need to be corrected. Results are documented and reported to top management.
Act
A key element of an ISO 50001 energy management program is the idea of continual and continuous improvement in energy performance. Therefore, the top management of an organization must have a process in place to periodically review. Then, evaluate both the company’s current energy program and its energy performance. Management must identify new opportunities, and take action for improvement.
On the road to digital transformation? Get our Free Digital Transformation Roadmap, a step-by-step guide to achieving data-driven excellence in manufacturing.
Receiving “ISO 50001 certification” requires review and certification by an official third party organization of all the procedures and documentation related to an energy management program. Furthermore, certification requires that a company actually meet its internally set goals for energy and total cost reduction. While an ISO certified energy program may be more complex than an internally developed program, it has the advantage that external guidance and verification may increase the internal importance and chances of success of a program. Additionally, the ISO certification should have a positive marketing influence. It is a clear indication to everyone inside and outside a company, including its customers, that a company is committed to saving energy and reducing the impact of its operations on the environment.
Conclusion
dataPARC offers a comprehensive suite of features designed to enhance energy management in manufacturing. Including real-time monitoring, advanced analytics, and seamless integration to ensure efficient and sustainable operations.
To get started with dataPARC, the onboarding process typically takes a few weeks, during which our team provides dedicated support for a smooth transition. Preparing your systems involves identifying key energy metrics and ensuring data sources are connected. Our experts guide you through setup, customization, and training, enabling your team to leverage dataPARC’s full capabilities quickly. By taking these steps, you’ll optimize energy usage and achieve your sustainability goals with dataPARC
ESG Environmental Excellence Guide
A comprehensive guide focusing on key environmental KPIs, strategic practices, and how software can support impactful environmental strategies for sustainable operational success.









