Manufacturers everywhere are being pushed to do more with less. Rising costs, shifting customer demands, and the need for real-time visibility are driving a major shift in how factories operate. However, while the concept of “smart manufacturing” may sound complex or overwhelming, getting started doesn’t have to be. Whether you’re beginning your digital transformation or looking to elevate your plant’s performance, this blog will walk you through the core technologies, benefits, challenges, and first steps to help you build a smarter, more connected factory, without the headaches.
Break Data Silos and Gain Real-Time Visibility Across Your Enterprise with PARCview
Why Smart Factories Matter Now
Manufacturing is transforming. Faced with evolving customer demands, global supply chain disruptions, labor shortages, and the push for sustainability. Companies are realizing that traditional, disconnected systems can no longer keep up. To stay agile and resilient, operations need to be smarter, faster, and more connected.
Smart factories offer a path forward. By integrating digital tools like IoT, machine learning, and real-time analytics into the production environment, manufacturers gain the ability to monitor processes continuously, make informed decisions faster, and respond to issues before they escalate.
The shift toward smart manufacturing isn’t just about technology; it’s about creating a more adaptive, data-driven culture across the plant. Whether you’re aiming to reduce downtime, improve product quality, or gain better visibility across operations, building a smart factory gives your team the tools they need to succeed today and scale tomorrow.
Key Technologies’ Power Smart Factories
Smart factories rely on a combination of advanced technologies that work together to enable real-time visibility, intelligent decision-making, and seamless automation. While each technology plays a unique role, it’s their integration that truly unlocks the potential of smart manufacturing. Below are some of the most critical technologies driving this transformation:
Internet of Things (IoT)
The foundation of a smart factory starts with connectivity. IoT devices, sensors, controllers, and smart equipment collect real-time data from across the production floor. This constant data stream enables centralized monitoring, remote access, and faster identification of abnormal conditions.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML take raw data and turn it into intelligence. From predicting equipment failures to optimizing quality control, these tools recognize patterns that would be difficult or impossible to spot manually. Over time, machine learning models improve, becoming more accurate and powerful as more data is processed. However, you need to be sure your site is set up to take advantage of such technology.
Big Data Analytics
Smart factories generate a massive volume of data. Big data analytics allows manufacturers to sift through this information efficiently, revealing trends, anomalies, and opportunities for optimization. It enables informed decision-making at every level, from operators on the floor to executive leadership.

Cloud Computing
Cloud platforms provide scalable storage and computing power for smart manufacturing initiatives. They make it easier to access data from multiple sites, collaborate across teams, and run advanced analytics tools, without the burden of on-prem infrastructure.
Digital Twins
A digital twin is a virtual representation of a physical process, system, or piece of equipment. By simulating real-world scenarios, manufacturers can test changes, predict outcomes, and troubleshoot issues without disrupting actual production. This leads to better planning and fewer costly surprises.
Core Components of a Smart Factory (What You Need in Place)
Smart factories are built on more than just advanced technology; they rely on strategic integration and thoughtful system design. Before layering on AI or predictive analytics, it’s critical to establish a solid foundation that ensures all your systems, data, and people are connected and aligned. Here are the key components every smart factory needs to get right:
Data Integration and Connectivity
At the core of every smart factory is a connected data ecosystem. Data silos, where lab, maintenance, and process data are stored in separate systems, slow down decision-making and create blind spots. A smart factory breaks down these silos by integrating data from across the plant into a centralized, accessible system.
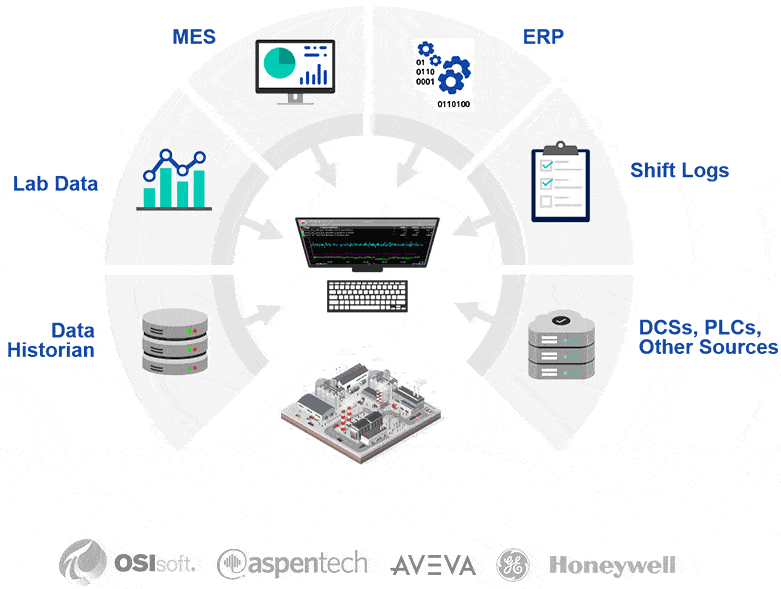
Data integration with dataPARC unifies information and makes it accessible from one centralized platform.
This connectivity enables real-time monitoring, faster troubleshooting, and more reliable reporting. It also ensures that operators, engineers, and leadership are working from the same source of truth.
Advanced Analytics and Machine Learning
Once your data is integrated, the next step is making sense of it. Smart factories use advanced analytics and machine learning to extract insights from historical and real-time data. These tools identify trends, highlight inefficiencies, and predict failures, so teams can act proactively rather than reactively.
Over time, machine learning algorithms become more accurate, helping to fine-tune processes, improve yields, and reduce unplanned downtime.
Digital Twins
A digital twin can range from a dynamic, virtual replica of a physical asset, process, or system to a real-time monitoring system of the system. It can allow teams to simulate different production scenarios, test changes safely, or forecast the impact of adjustments without disrupting operations. It allows for the monitoring of the asset from a remote location.
This kind of real-time monitoring is invaluable for continuous improvement, capacity planning, and identifying issues before they affect production.
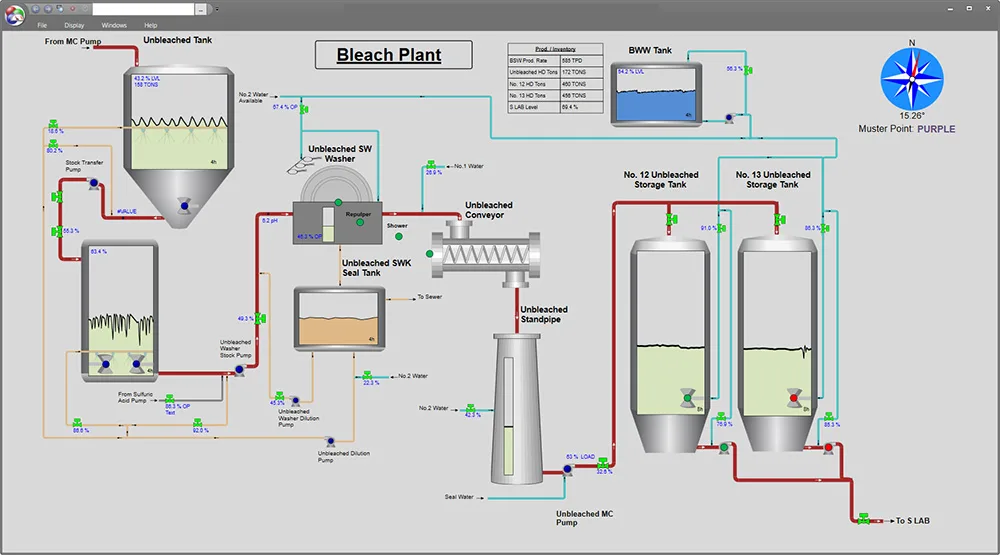
This process overview graphic is one example of a digital twin. Real-time data from physical assets is mirrored virtually. This type of digital twin helps operators monitor and optimize processes for improved performance and decision-making.
Process Automation
Automation is a cornerstone of smart manufacturing; not just robotics, but also tasks like report generation, inventory updates, and alarm responses. By automating repetitive or time-sensitive processes, manufacturers can reduce errors, improve consistency, and free up staff to focus on higher-value work.
Smart automation also improves adaptability. When integrated with analytics and visualization tools, automated systems can adjust based on real-time conditions.
These components work best when deployed together. A connected, automated environment powered by accurate data and predictive insight helps manufacturers adapt quickly, optimize continuously, and operate more intelligently.
The Benefits: Why Smart Factories are Worth it
Smart factories offer more than just upgraded tools. They create a connected, efficient environment where decisions are faster, processes are more reliable, and teams can act with confidence.
With integrated systems and real-time visibility, manufacturers can reduce downtime, catch quality issues earlier, and make better use of resources. These improvements not only lower costs but also support long-term growth and adaptability in a fast-changing market.

Explore the path to smarter manufacturing. Get your copy of Building the Smart Factory today.
Real-World Challenges & How to Avoid Them
Adopting smart manufacturing can come with hurdles. Many plants face issues when trying to connect modern tools to older systems. Integration takes planning, and not all platforms work well together.
Cybersecurity is another concern. More connectivity means more exposure, so it is important to protect your data and systems from external threats.
Workforce training is also key. Teams need support and tools that are easy to use. Choosing software with a user-friendly interface can reduce training time and ease adoption.
Finally, the upfront investment can feel overwhelming. Start small, prove value early, and scale at your own pace.
Your Step-by-Step Smart Factory Kickstart Plan
Starting your smart manufacturing journey doesn’t need to be overwhelming. Here’s a simple roadmap to help you move forward with clarity and purpose.
- Evaluate Your Current Operations
Take stock of your existing systems, data sources, and pain points. Identify areas where better visibility or automation would make an immediate impact. - Set Clear Goals
Decide what success looks like. Common goals include reducing downtime, improving product quality, or streamlining manual reporting - Choose the Right Tools
Select technologies that fit your goals and work with your existing infrastructure. Look for solutions that offer flexibility and ease of integration. - Start Small
Begin with one line or process area. Prove the value, then expand based on what works. - Train and Support Your Team
Make sure your team is ready to use new tools. Choose platforms that are intuitive to reduce the learning curve - Monitor, Adjust, and Scale
Track results. Use what you learn to improve, expand, and bring more value to other parts of the plant.
How dataPARC Simplifies the Journey
Implementing smart manufacturing doesn’t have to mean starting from scratch. dataPARC helps teams take meaningful steps forward by building on the systems they already have in place.
Works with What You Have
dataPARC integrates easily with existing systems, making it easier to connect data from process historians, lab systems, and equipment without major infrastructure changes.
Real-Time Visualization
From interactive dashboards to detailed trends and graphics, dataPARC gives users a live view of their plant. This helps teams spot issues faster, monitor KPIs, and make confident decisions in the moment.
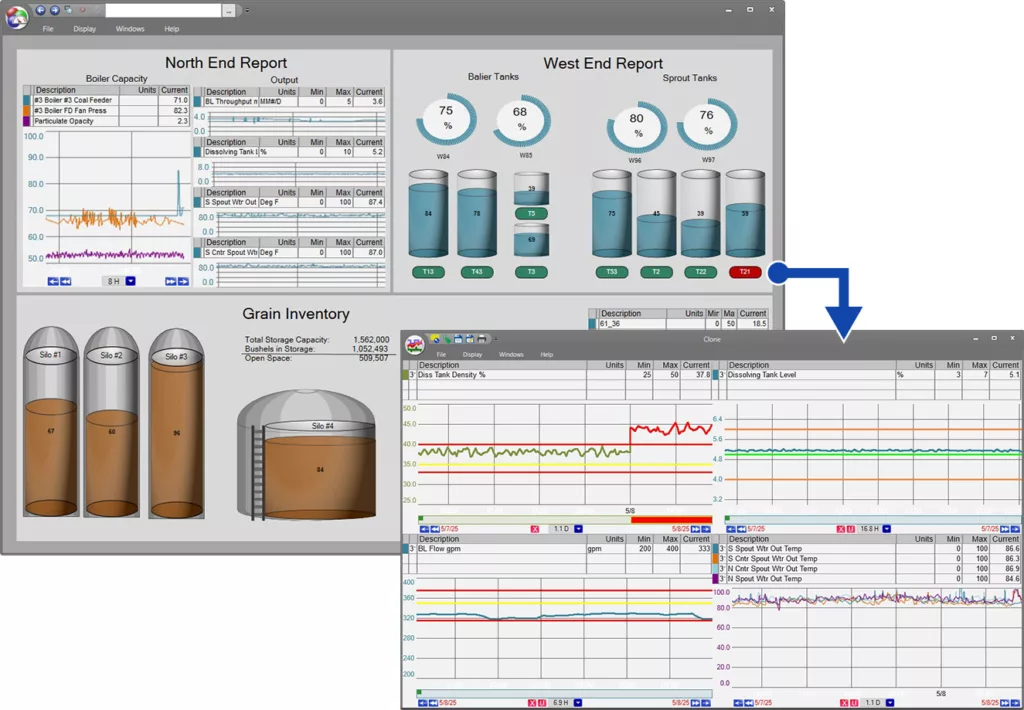
A real-time dashboard highlights an out-of-spec tank. With one click, operators can pull up detailed trends to quickly diagnose the issue.
Scalable and Cost-Effective
With tag-based licensing and unlimited user access, dataPARC allows you to start in one area and expand at your own pace—without the pressure of large upfront costs.
User-Friendly and Operator-Focused
Designed for engineers and operators, dataPARC is intuitive and flexible. It reduces the training burden and gets teams up and running quickly, even in high-turnover environments.
Built for Action
Whether you’re tracking alarms, running reports, or feeding data to AI tools, dataPARC brings all your information together to support fast, informed decisions and drive continuous improvement.
Final Thoughts: Start Small, Think Big
Building a smart factory doesn’t happen overnight. The most successful transformations begin with a clear goal, a small pilot, and the right tools to support growth over time.
Focus first on visibility and integration. Once your data is flowing and your team can act on it, implementing more advanced tools like AI and digital twins becomes much easier.
Smart manufacturing is not just a project; it’s a mindset. By starting with the basics and scaling with intention, you can create a more connected, efficient, and resilient operation that’s ready for whatever comes next.
FAQ: Building A Smart Factory
1. What is a smart factory?
A smart factory is a highly digitized and connected production facility that uses real-time data, automation, and advanced analytics to optimize operations, improve efficiency, and support continuous improvement.
2. Why should manufacturers invest in smart factories?
Smart factories reduce costs, increase productivity, and improve quality by providing visibility into every step of the production process. They also help manufacturers adapt to market changes faster and meet sustainability goals.
3. What technologies are used in a smart factory?
Key technologies include IoT sensors, data historians, advanced analytics, AI/ML, robotics, and manufacturing execution systems (MES). dataPARC covers many of these, and together these create a connected ecosystem for real-time monitoring and decision-making.
4. How do you start building a smart factory?
Most companies begin by integrating data sources and improving visibility. Establishing a reliable data foundation, such as integrating process, quality, and environmental data into a single platform, is often the first step before adding more advanced capabilities.
5. What role does data play in a smart factory?
Data is the backbone of a smart factory. It enables real-time monitoring, predictive analytics, and automated control. Without a unified view of data across IT and OT systems, smart factory initiatives can stall or fail to scale.
6. What challenges do companies face when transitioning to a smart factory?
Common challenges include siloed data, high upfront investment, cybersecurity concerns, and employee adoption. These can be addressed with phased implementation, strong change management, and the right data infrastructure.
Building The Smart Factory
A Guide to Technology and Software in Manufacturing for a Data-Drive Plant